EVGA Z170 Classified K Motherboard Review
EVGA Z170 Classified K Overview and Test System
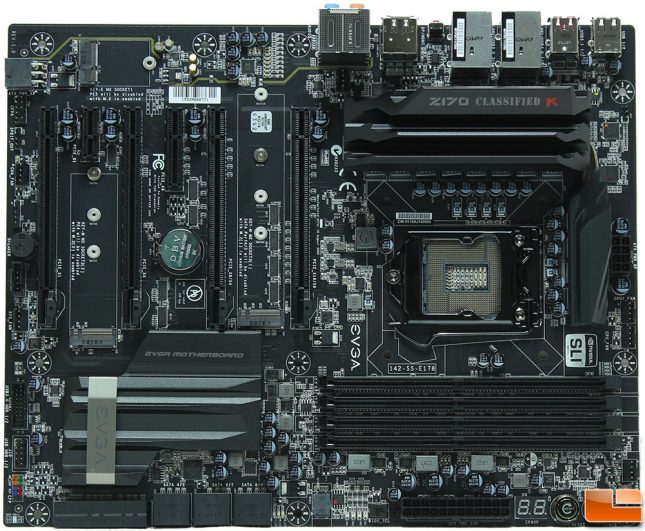
With only having three ATX motherboards for the Z170 chipset, the Z170 FTW, Z170 Classified K, and Z170 Classified 4-Way, they look nearly identical. There are differences of course with the change in functionality, but the overall look is nearly identical. Many of the features on the Z170 FTW are found on the Z170 Classified K, and those have been expanded on. In the lower right corner, EVGA has placed a Power and Reset button directly on the motherboard, along with a Dr Debug post code reader, which will also show the CPU temperature once it boots.
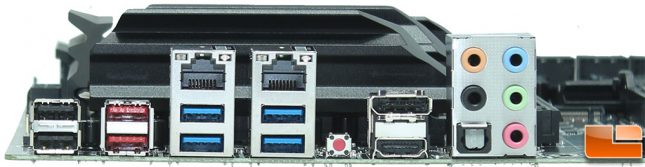
The Z170 Classified K has a fairly typical layout for the rear I/O cluster. On the far left, we start out with 2x USB 2.0, then move to 2x USB 3.1. The first ethernet connection is the Intel i219 NIC, which sits above 2x USB 3.0 ports. The Killer E2400 NIC is next, which again sits above 2x USB 3.0. For those that might encounter a BIOS issue, EVGA has an external reset button on the rear I/O cluster. Video support is provided by Display Port 1.2 and HDMI 1.4. The audio ports and Optical out are in the final group of ports.
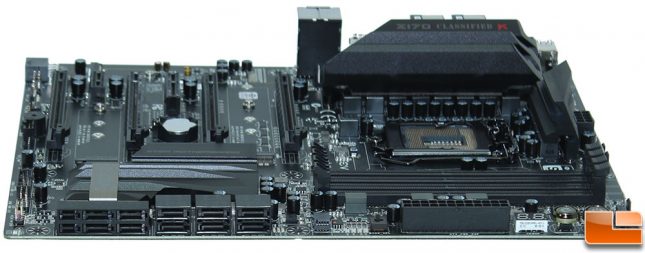
The Z170 Classified K has expanded the SATA offerings from just six SATA ports to now having a maximum of 10 SATA ports! In addition, the SATA connection cluster has been expanded to also include two SATA Express ports, which will each take up two SATA ports. Behind the SATA ports, they are numbered from the left, 0/1, 2/3, 4/5, 6/7, 8/9.
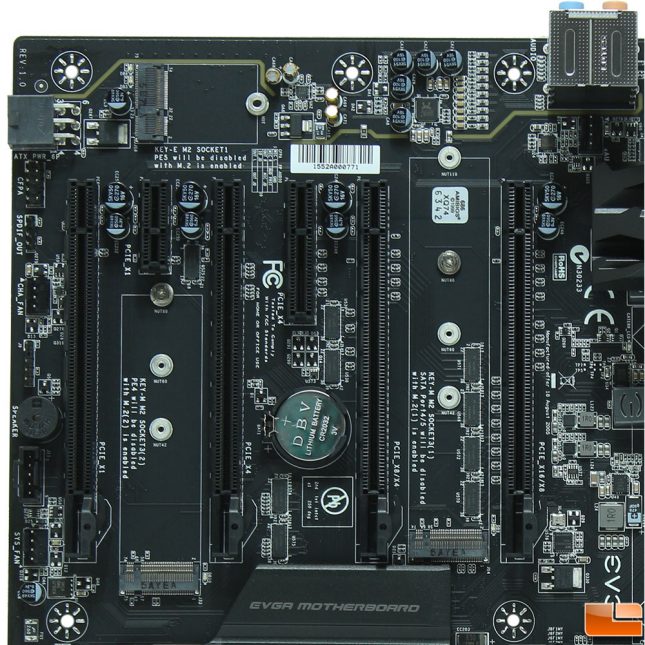

EVGA labels each of their PCIE slots so you know what it’s capabilities are. From the main PCIE slot on the right, it is listed as x16/x8, then we find an x8/x4, x4, x4, x1 and x1. The first three PCIE slots are powered from the CPU, while the other three on the left come from the PCH. Nestled between the PCIE slots are two of the three M2 slots, these two are Key M and are both capable of speeds up to 32Gbps. The third M2 slot is found just above the PCIE slots, and is a Key E slot typically used for WiFi cards, not storage. All of the M2 slots share their bandwidth with other ports, which will be disabled when using a M2 card, the motherboard clearly lists what will be disabled, otherwise you can reference the manual.
